What is CT Screening?
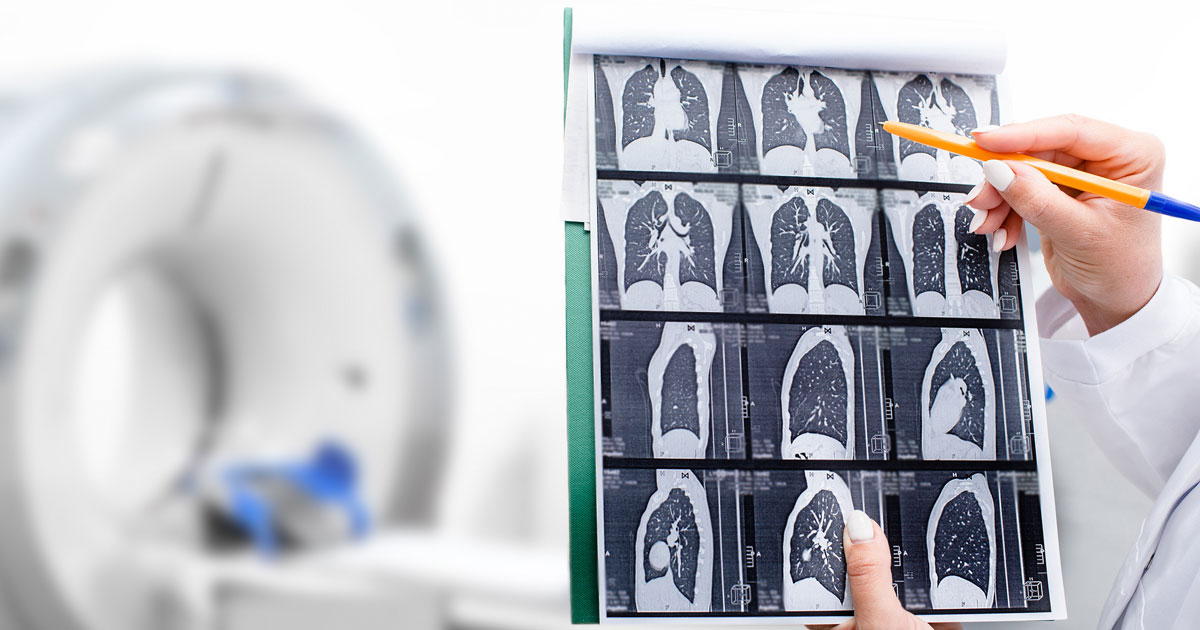
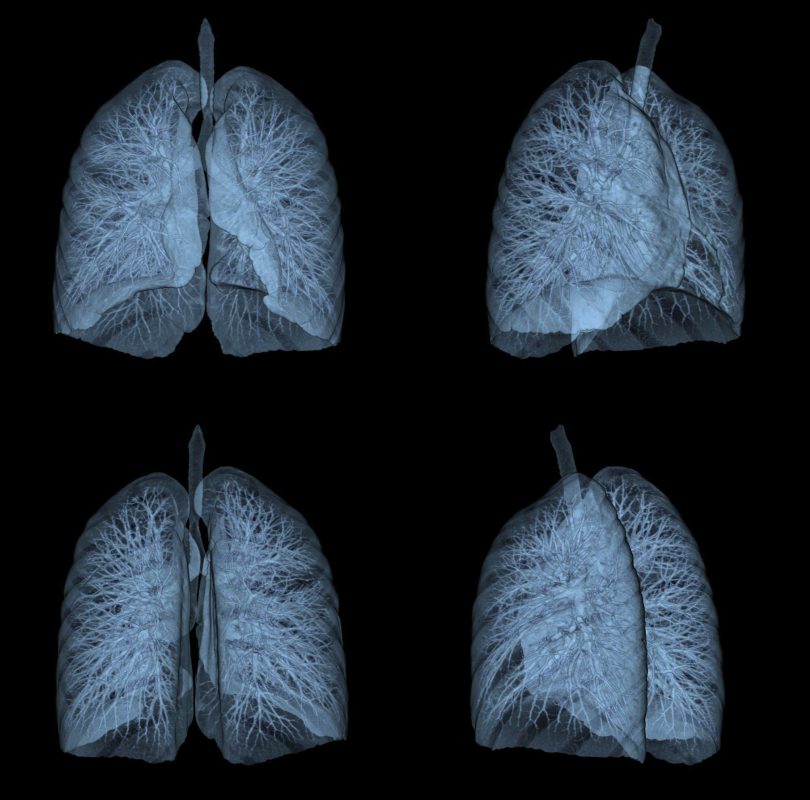
CT screening, also known as computed tomography screening, is a medical imaging technique that provides physicians with detailed images of the body’s interior. It creates cross-sectional images, or slices, of the body using a combination of X-rays and computer technology. These images can then be utilized for the diagnosis and monitoring of a variety of medical conditions. CT screening has become an indispensable tool in contemporary medicine, allowing doctors to detect and treat diseases at an early stage.
CT screening’s ability to provide detailed images of the body’s internal structures is one of its primary advantages.
This level of detail enables physicians to detect anomalies that may not be visible on other imaging tests, such as X-rays or ultrasounds. For instance, CT screening can detect tumors, blood clots, and infection-related symptoms in various organs and tissues. This early detection is essential for effective treatment and can substantially improve patient outcomes.
In addition to its diagnostic capabilities, CT screening is used to monitor the progression or treatment response of specific medical conditions. Patients with cancer, for instance, may undergo regular CT scans to determine the size and spread of tumors and the efficacy of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. By keeping track of changes over time, physicians can make informed decisions about treatment plans and adjust therapies accordingly.
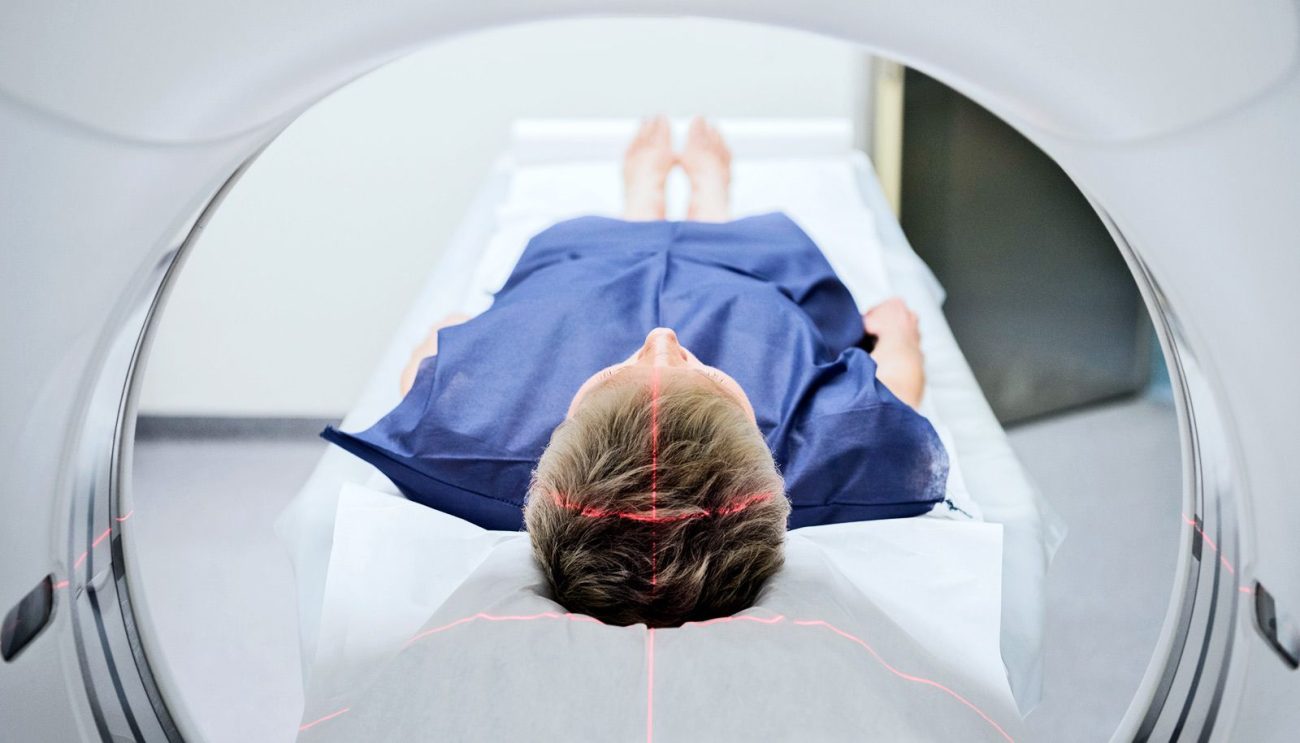
In addition, CT screening is a noninvasive, relatively quick, and painless procedure. The patient is positioned on a table that is moved through a large, doughnut-shaped CT scanner.
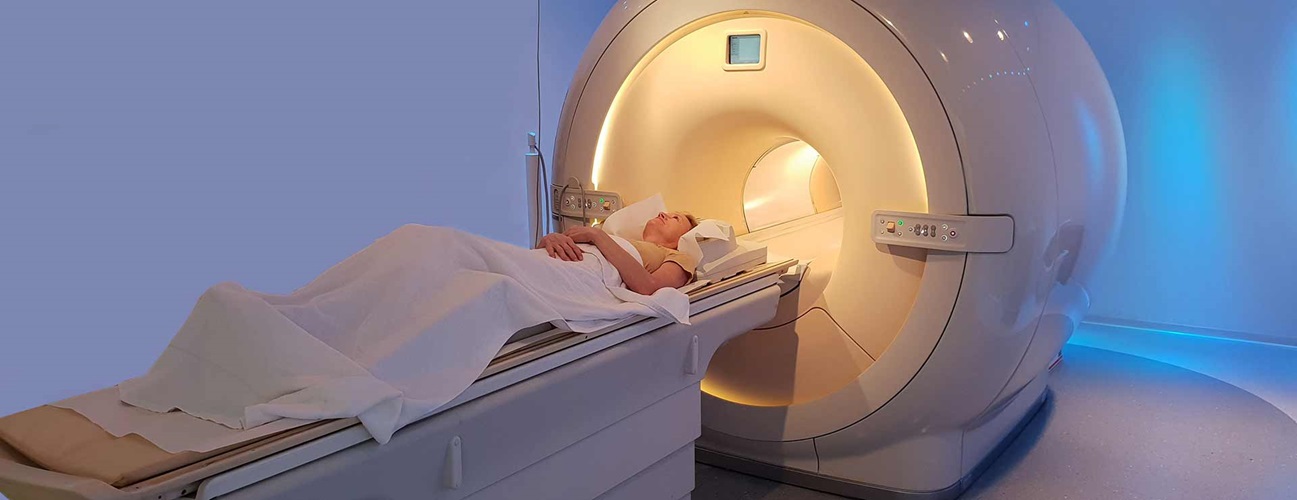
Multiple X-ray beams rotate around the body inside the scanner, capturing images from various angles. The entire process typically takes less than 30 minutes, and no special preparation is required beforehand. This makes CT screening a convenient option for patients and lessens the discomfort and anxiety associated with more invasive procedures.
It is essential to note, however, that CT screening involves exposure to ionizing radiation, which carries certain risks. Although the amount of radiation used in a single CT scan is deemed safe, repeated exposure can increase the risk of developing certain cancers over time. Before recommending CT screening, medical professionals weigh the potential benefits against the associated risks. In addition, they consider age, gender, and medical history to ensure that the benefits outweigh the potential risks.
In conclusion, CT screening is a valuable tool in modern medicine that allows doctors to obtain detailed images of the body’s interior for diagnostic and monitoring purposes. Its ability to detect abnormalities and monitor changes over time contributes to earlier detection and better patient outcomes. The potential risks associated with ionizing radiation should be carefully considered, despite the fact that the procedure is noninvasive and convenient. Overall, CT screening is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of numerous medical conditions.