What is ultrasonography ?
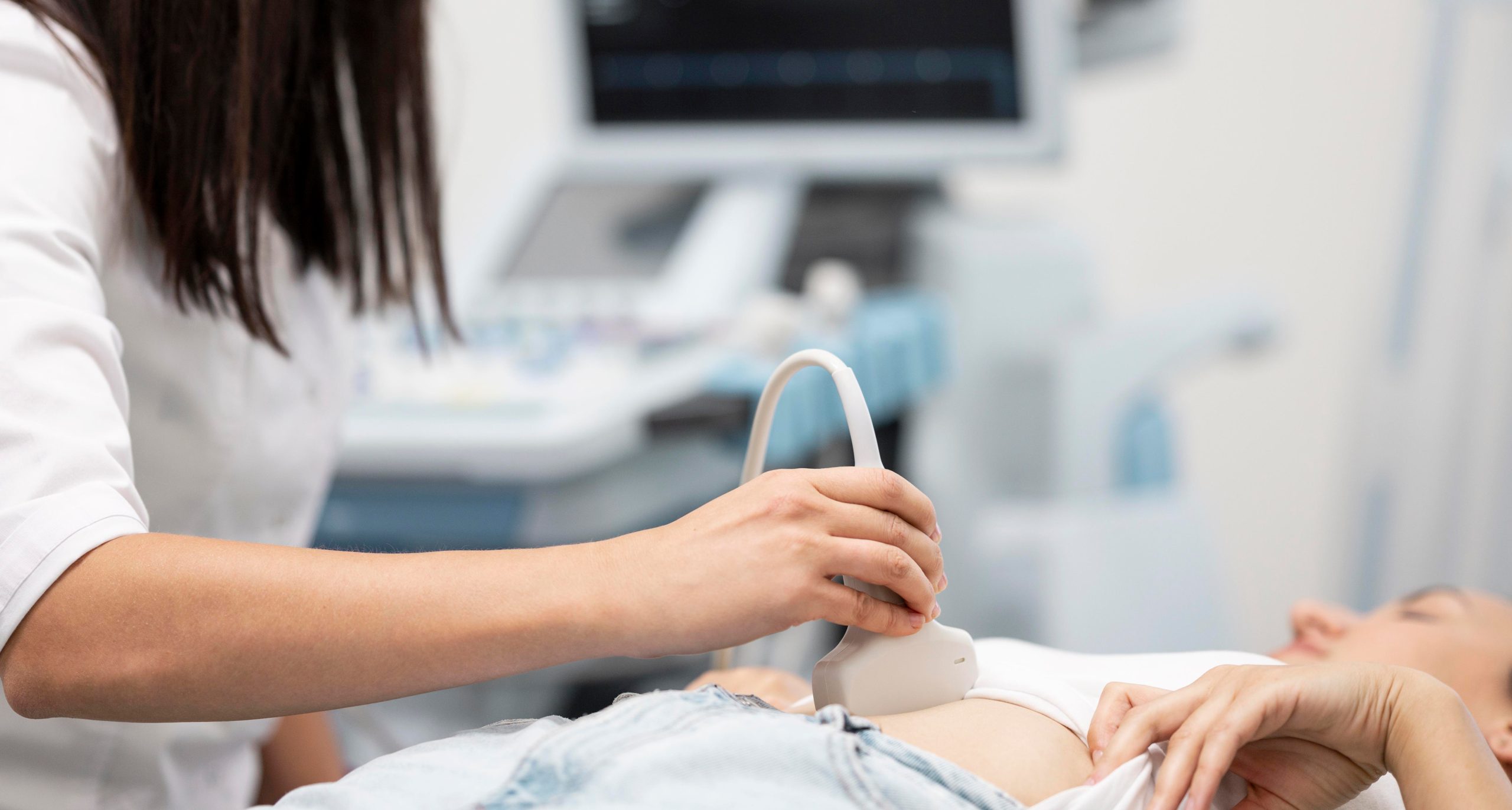
Ultrasonography (USG), also known as ultrasound imaging, is a diagnostic medical technique that produces images of the inside of the body using high-frequency sound waves. It is a non-invasive and safe procedure that allows doctors to see organs, tissues, and blood vessels in real time. USG is commonly used in obstetrics, gynecology, cardiology, and radiology to aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of various conditions.
One of the primary benefits of USG is its ability to provide detailed images of soft tissues and internal organs without requiring surgery or ionizing radiation exposure. It employs sound waves with higher frequencies than those audible to the human ear. These sound waves are transmitted into the body via a transducer, which also receives the echoes produced by the sound waves’ interaction with various tissues. A computer then processes the echoes to produce real-time images on a monitor.
Obstetric ultrasound can provide information about the fetus’s size, position, and health, as well as identify any potential complications like ectopic pregnancies or placenta previa. It can also assist in determining the gestational age and estimating the due date. The images obtained through USG allow healthcare professionals to assess both the mother’s and the baby’s well-being throughout the pregnancy.
USG is widely used in a variety of medical specialties other than obstetrics. It can provide valuable information about the structure and function of the heart in cardiology. Echocardiography, a type of USG, allows doctors to examine the heart’s valves, chambers, and blood flow patterns. This information is critical in the diagnosis and management of a variety of cardiac conditions, such as heart valve disorders and congenital heart defects.
Abdominal ultrasound can aid in the detection of gallstones, liver diseases, and kidney or pancreas abnormalities. Musculoskeletal ultrasound can help with the diagnosis of injuries or conditions affecting the muscles, tendons, or joints. Furthermore, USG-guided procedures are frequently used to guide biopsies or drain fluid collections from various parts of the body.
Because it can provide real-time images of internal structures without requiring the use of ionizing radiation or other invasive procedures, ultrasonography is an extremely useful tool in contemporary medicine. This is due to the fact that it can provide these images. It is an essential diagnostic tool in a wide variety of medical fields due to the fact that it can be used in a variety of medical settings without risk. As technology improves, ultrasonography will almost certainly become more sophisticated and will likely be incorporated into standard medical practice.