What is blood analysis?
Whole blood analysis is the process of examining and evaluating the various components of a whole blood sample. This type of analysis provides valuable insight into an individual’s overall health and can aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of a variety of medical conditions. The analysis involves examining the various blood cell types, measuring their numbers, and evaluating their functionality. In addition, it involves determining the concentrations of various chemical substances, such as glucose, cholesterol, and electrolytes. The analysis of whole blood is an indispensable tool in clinical laboratories and plays a crucial role in the management and treatment of disease.
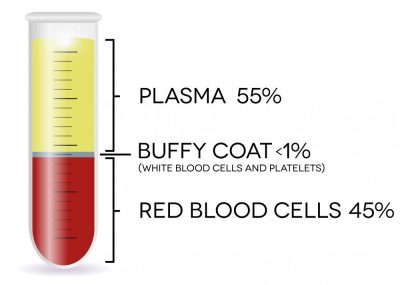
Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count (CBC) is one of the primary components analyzed in whole blood. The CBC provides information regarding the number and types of blood cells, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. By analyzing these parameters, healthcare professionals are able to evaluate a patient’s overall health, identify any abnormalities, and track the progression of certain diseases. A decrease in the number of red blood cells may indicate anemia, whereas an increase in the number of white blood cells may indicate an infection or inflammation.
In addition to measuring cell counts, the analysis of whole blood also includes the measurement of various chemical substances.
Glucose levels are frequently measured to assess blood sugar control and diagnose diabetes. Cholesterol levels are significant indicators of cardiovascular health and can aid in determining the risk of heart disease. Electrolyte levels, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, are essential for maintaining normal bodily functions and can shed light on conditions such as dehydration and kidney disorders.
Typically, whole blood analysis is conducted in a clinical laboratory using automated analyzers and specialized techniques. These analyzers utilize advanced technology to precisely measure various blood sample components. The procedure entails removing a small amount of blood from a vein, typically in the arm, and placing it in specialized tubes or containers for analysis. Using specific reagents and instruments, the samples are then processed to obtain accurate results.
Healthcare professionals, including physicians and laboratory technicians, interpret the results of whole blood analysis.
They compare the values obtained from the analysis to predetermined reference ranges to ascertain the presence of abnormalities. These abnormal values can then be used to diagnose medical conditions and track the progress of treatment. In some instances, additional testing or consultations may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis or determine an appropriate course of treatment.
In conclusion, whole blood analysis is an essential component of medical diagnostics that provides valuable information about a person’s overall health condition. By analyzing the various components present in a blood sample, medical professionals can diagnose and monitor a variety of diseases. The analysis involves counting cells and evaluating their functionality, as well as measuring the concentrations of various chemicals. With the aid of automated analyzers and specialized techniques, medical decision-making can be guided by precise results. The analysis of whole blood plays a vital role in disease management and treatment and significantly improves patient outcomes.